Blue Light Skincare: Separating Hype from Science
With the increasing reliance on digital devices in our daily lives, the cosmetic industry has witnessed a growing interest in blue light skincare treatments. As our screen time rises, especially in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, the industry recognizes the need to address potential skin damage caused by blue light exposure. In this article, we delve into the world of blue light and its effects on our skin. Blue light, a high-energy visible light (HEV) falling within the visible light spectrum, is emitted by digital devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. Unlike UVA and UVB rays, which are known for their harmful effects on the skin, blue light has a shorter wavelength but higher energy. This unique property has raised concerns regarding its potential impact on skin health.
Studies have suggested that blue light can penetrate the skin more deeply than UV radiation, reaching the underlying layers. This deeper penetration may trigger oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially leading to premature skin aging, hyperpigmentation, and other skin concerns. However, it is important to note that further research is needed to fully understand the extent of blue light’s impact on the skin.
Suncreens formulated with Titanium dioxide and Zinc oxide have long been recognized for their remarkable ability to provide effective protection against the harmful UVA/UVB rays that can wreak havoc on our skin. However, when it comes to shielding our delicate skin from HEV (High Energy Visible) light, their efficacy tends to diminish. Fortunately, a groundbreaking study published recently in the esteemed Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology has uncovered a fascinating development in the realm of sun protection. This pioneering research delved into the potential of incorporating red, yellow, and black iron oxides as active ingredients in sunscreens. These iron oxides, known for their vibrant hues, displayed promising characteristics in attenuating, or effectively shielding, the skin from the pernicious effects of blue light. By harnessing the power of these iron oxides, sunscreens could potentially offer enhanced protection against skin damage, such as premature aging, caused by exposure to blue light. As the scientific community delves deeper into the potential of iron oxide-based sunscreens, we can look forward to a future where our skin remains shielded from the detrimental effects of blue light, preventing premature aging and maintaining its youthful radiance. The quest for optimal sun protection continues, and with each new breakthrough, we inch closer to achieving healthier and more resilient skin for generations to come.
Have you ever wondered about the detrimental effects of blue light on our skin? In this discussion, we will not only explore the impact of blue light but also delve into the theories and scientific evidence behind its potential to damage our skin. Additionally, we will examine the fascinating concept of utilizing familiar ingredients, like antioxidants, to provide a protective shield for our skin while we engage in late-night activities such as video chatting on platforms like Zoom, scrolling through social media, or indulging in online shopping extravaganzas.

Blue Light Skincare: Separating Hype from Science
What is blue light?
Blue light, a form of electromagnetic radiation, occupies a specific range of wavelengths and can be categorized based on its position within the energy spectrum. Falling within the visible light spectrum, blue light encompasses wavelengths ranging from 400 to 525 nanometers (nm) and resides in the high-energy wavelength (HEV) band.
Throughout our lives, we encounter various forms of electromagnetic radiation on a daily basis. Consider the likes of X-rays, microwaves, UV rays, and radio waves. Among these waves, sunlight emerges as the most pervasive, exposing us to significant amounts of blue light. Interestingly, the reason we perceive the sky as blue lies in the refraction of shorter blue light wavelengths by Earth’s atmosphere.
In addition to sunlight, blue light also emanates from a multitude of artificial sources, such as LED lights and electronic devices including laptops, televisions, and mobile devices. LED lights, in particular, emit blue light, and interestingly, this type of light has found application in acne treatment. By potentially reducing the activity of sebaceous glands and subsequently limiting sebum production, blue light LED exposure has been explored as a means to address acne-related concerns.
As we navigate through our modern lifestyles, it becomes increasingly evident that exposure to blue light extends beyond natural sources. The widespread use of electronic devices and the prevalence of artificial lighting have heightened our daily encounters with blue light. Recognizing the potential impact of this pervasive light on our skin, it becomes imperative to consider protective measures that can safeguard our skin from its potential adverse effects.
What is blue light?
Is blue light a skincare issue?
The pervasive use of screens and electronic devices emitting blue light has become a relatively recent phenomenon, prompting researchers to delve into its potential impact on skin health. As we find ourselves in a world governed by strict lockdowns and social distancing measures, our reliance on digital devices has soared, becoming the primary means of maintaining social connections, conducting work, and engaging in online shopping. In fact, studies reveal that internet usage has skyrocketed by 40% to 100% globally compared to pre-lockdown levels.
Consequently, a significant portion of our daily lives is now spent in front of screens that emit blue light, not only during the pandemic but also in our regular routines. The reliance on mobile devices and desktop hardware has become ingrained in our working and educational lives. The profound changes brought about by the pandemic and our continuous shift towards digital communication are expected to endure, shaping our way of life in unprecedented ways. The question arises: should we be concerned about the implications of this excessive exposure to blue light? As we navigate this digital landscape, it becomes essential to understand the potential effects of blue light on our skin health and take appropriate measures to mitigate any risks that may arise.
While research in this field is still emerging, some studies have suggested a possible correlation between prolonged exposure to blue light and skin concerns. It is believed that blue light can penetrate the skin more deeply than UV rays, potentially triggering the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and contributing to oxidative stress. This oxidative stress can disrupt the skin’s natural balance, leading to inflammation, hyperpigmentation, and potentially even accelerating the aging process.
In a thought-provoking statement featured in the renowned UK newspaper, The Guardian, Stuart Peirson from the Sleep and Circadian Neuroscience Institution (SCNi) at Oxford University shed light on the nature of blue light. Peirson emphasized that blue light itself is not inherently sinister. In fact, the blue part of the light spectrum experiences significant changes during dawn and dusk, and our bodies have evolved to detect and respond to these variations as they play a vital role in setting our internal clocks. However, as Peirson pointed out, the proliferation of light-emitting devices in our environment and our increasing reliance on them have created a scenario where exposure to blue light has become pervasive and addictive.
It is essential to approach the subject of blue light and its potential effects on the skin with caution and an open mind. Remember that not all adverse effects experienced from extended screen time can be directly attributed to blue light alone. For instance, deteriorating eyesight after prolonged screen usage may be the result of factors such as dry eyes, incorrect eyeglasses, or simply fatigue. The impact of blue light on both eye health and skin damage remains subjects of ongoing debate and research.

Is blue light a skincare issue?
What are the effects of blue light on skin?
The extent of conclusive and independent scientific research conducted thus far on the effects of blue light on the skin remains limited compared to the extensive research conducted on UVA/UVB rays and the efficacy of sun protection ingredients in skincare products.
In 2010, a research study aimed to examine the impact of blue light on normal skin, specifically focusing on photodamage, skin aging, and melanogenesis. Surprisingly, the study did not find evidence to support the notion that visible blue light directly caused premature aging of the skin. However, subsequent research has indicated that blue light may indeed contribute to skin aging processes, sharing similarities with the effects induced by UVA exposure. This emerging understanding reflects the evolving nature of research in this field, which has accelerated in response to the substantial increase in our daily screen time over the past decade. The continuous advancements in technology and our increased reliance on electronic devices have propelled the need for further investigation into the potential effects of blue light on the skin. As our habits and behaviors have evolved, it is imperative that scientific research keeps pace with these changes in order to provide comprehensive insights into the impacts of blue light exposure on skin health.
In more recent times, additional research conducted in 2019 has shed further light on the disruptive effects of blue light on our Circadian rhythm and its impact on skin cells. This research unveiled that blue light emissions possess the capability to interfere with the inner “bio-clock” or Circadian rhythm of our skin cells. The study revealed that epidermal skin cells have the remarkable ability to directly sense light and regulate their own clock gene expression. When exposed to blue light, these cells are triggered to perceive it as daytime, even during nighttime hours. Consequently, this disruption impairs the cells’ capacity to utilize the restorative benefits of sleep during the darkness to carry out their normal functions of repair and overall skin maintenance.
The research exploring the relationship between iron oxides and blue light emphasizes the role of high-energy visible (HEV) light in contributing to premature aging by interfering with essential cellular processes. This connection serves as a significant link between blue light exposure and its potential impact on the health of our skin. By impeding normal cellular functions, HEV light poses a potential threat to our skin’s overall well-being and can disrupt its natural processes, thereby increasing the risk of premature aging. Understanding and addressing this connection is crucial in our efforts to safeguard and maintain the health and vitality of our skin.
As mentioned earlier, the study conducted in 2019 reached a significant conclusion regarding the effects of blue light on the skin. It was found that blue light exposure has the potential to heighten the production of free radicals, induce DNA damage, and trigger the release of inflammatory mediators. These deleterious effects have the capacity to accumulate over time, leading to an overall increase in skin damage and ultimately accelerating the aging process. This highlights the importance of recognizing and addressing the potential harmful effects of blue light on our skin to mitigate long-term consequences and promote skin health.
If we continue to use our devices that emit blue light well into the late evening, or worse, if we switch them on in complete darkness with their backlighting activated, it is important to be aware of the potential consequences. Night owls should take caution, as such habits are likely to disrupt our Circadian rhythm, negatively impacting our sleep patterns. Furthermore, this disruption compromises the skin’s ability to undergo the essential processes of repair and renewal that are typically facilitated by the conducive environment provided by darkness and restful sleep. It is crucial to be mindful of our device usage habits, especially during the evening and nighttime hours, to promote healthy sleep patterns and allow our skin cells to effectively rejuvenate and restore themselves.

What are the effects of blue light on skin?
Conclusions on blue light skincare treatment
In the realm of blue light skincare, two primary approaches can be observed. The first approach involves the use of topical ingredients that aim to filter, absorb, or attenuate blue light, thereby preventing its absorption into the skin. These mechanisms are akin to how sunscreens operate, providing a protective barrier against blue light.
The second approach focuses on enhancing the skin’s natural cellular repair processes and reducing the oxidative stress induced by blue light. This is achieved through the utilization of ingredients rich in antioxidants. By incorporating antioxidant-rich ingredients into skincare products, the aim is to bolster the skin’s defense against the potential harmful effects of blue light exposure and promote overall skin health.
There is a growing presence of cosmetic ingredients in the market that are specifically designed to filter blue light. Some of these innovative ingredients make use of botanical extracts. One such example is the incorporation of carotenoids, which are phytonutrients responsible for the vibrant red, yellow, and orange hues found in various fruits and vegetables, with carrots being a notable source. Carotenoids have the remarkable ability to absorb the blue light spectrum, making them effective in filtering out this type of light. Additionally, they also serve as antioxidants, further contributing to the overall protection and well-being of the skin. The inclusion of carotenoid-based ingredients in skincare formulations showcases the continuous efforts to provide effective blue light protection while harnessing the beneficial properties of natural botanical extracts.
Before making any claims about the role of specific cosmetic ingredients in blue light and sun protection skincare, it is essential to conduct thorough research. It is important to note that the research conducted on individual ingredients does not automatically translate into claims about how those ingredients function within a final skincare product. To substantiate claims about a product’s efficacy in directly combating blue light, clinical tests on the finished cosmetic formulation would be necessary.
The future of anti-blue light skincare is complex and requires careful examination based on sound scientific principles. Currently, it appears that maintaining and even intensifying our sun protection measures remains crucial. Additionally, ensuring a sufficient amount of quality sleep, typically 7-8 hours with all lights off, is essential to support skin renewal and repair. As for brands promoting their products as anti-blue light skincare, the ultimate decision lies with consumers and their assessment of the available information.
It is important for us to closely monitor the developments in the blue light skincare space and remain attentive to future research findings. By staying informed, we can continue to navigate this evolving field and make well-informed decisions regarding skincare practices and product choices.

Conclusions on blue light skincare treatment
Exploring Its Applications in Skincare
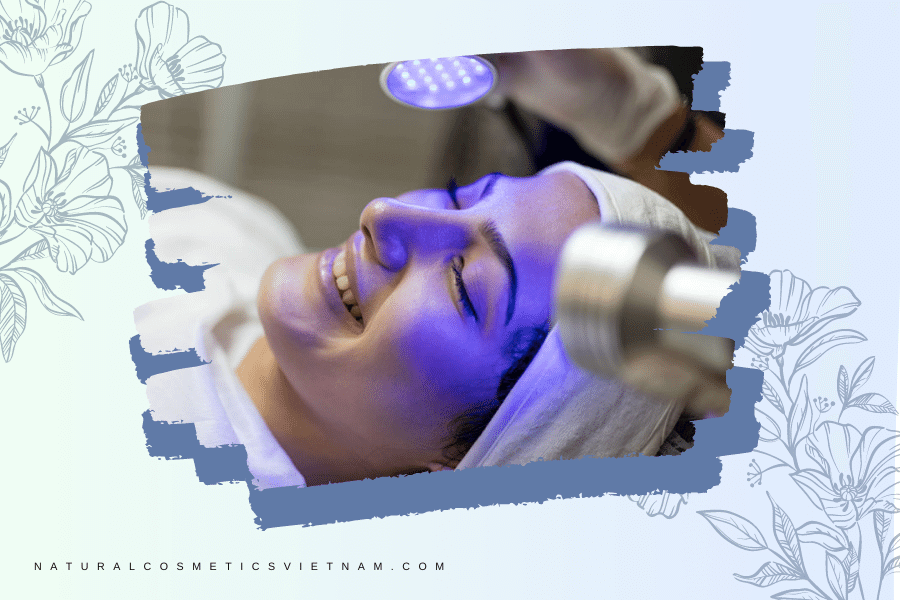
In recent years, the beauty industry has embraced the potential benefits of blue light in skincare treatments. Blue light therapy, also known as photodynamic therapy, has gained popularity for its ability to address various skin concerns. This article delves into the applications of blue light in beauty treatments, highlighting its effectiveness in acne treatment, skin rejuvenation, hyperpigmentation, oil control, and wound healing.
Acne Treatment
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. While several treatment options exist, the emergence of blue light therapy as a promising solution has sparked significant interest in the beauty and skincare industry. This article explores the potential of blue light therapy in acne treatment, highlighting its mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety considerations.
Blue light therapy utilizes a specific wavelength of light, typically between 415 to 450 nanometers, to target and destroy the bacteria responsible for acne breakouts. This wavelength penetrates the skin’s surface, reaching the sebaceous glands where the bacteria thrive. By inducing a chemical reaction that generates singlet oxygen molecules, blue light effectively eliminates the acne-causing bacteria without harming the surrounding healthy tissues. The primary target of blue light therapy is Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a bacterium that contributes to the formation of acne. When exposed to blue light, the bacteria absorb the light energy, which triggers the production of toxic compounds that lead to their destruction. Additionally, blue light therapy helps reduce inflammation and sebum production, further aiding in the treatment and prevention of acne lesions.
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of blue light therapy in acne treatment. Research has shown significant reductions in both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions after a series of blue light treatments. In some cases, blue light therapy has been found to be equally effective as traditional acne medications, providing a non-invasive alternative for individuals who prefer non-pharmaceutical interventions. Blue light therapy is generally considered safe and well-tolerated. Unlike some other acne treatments, such as oral medications, blue light therapy does not have systemic side effects. However, it is important to protect the eyes from direct exposure to the light source during treatment. Therefore, wearing protective eyewear or covering the eyes is typically recommended. Blue light therapy can be incorporated into a comprehensive skincare routine for individuals with acne-prone skin. It is often used in combination with other acne treatments, such as topical creams or cleansers, to enhance overall efficacy. Consulting with a dermatologist or skincare professional is advisable to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and frequency of blue light sessions based on individual skin needs.
Blue light therapy represents a promising advancement in acne treatment, offering a non-invasive, safe, and effective solution for individuals struggling with acne breakouts. By targeting the acne-causing bacteria and reducing inflammation, blue light therapy helps alleviate symptoms, improve skin condition, and enhance overall self-confidence. While further research is still underway to explore its long-term effects, blue light therapy stands as a valuable addition to the arsenal of acne treatment options available to dermatologists and skincare professionals.
Exploring Its Applications in Skincare
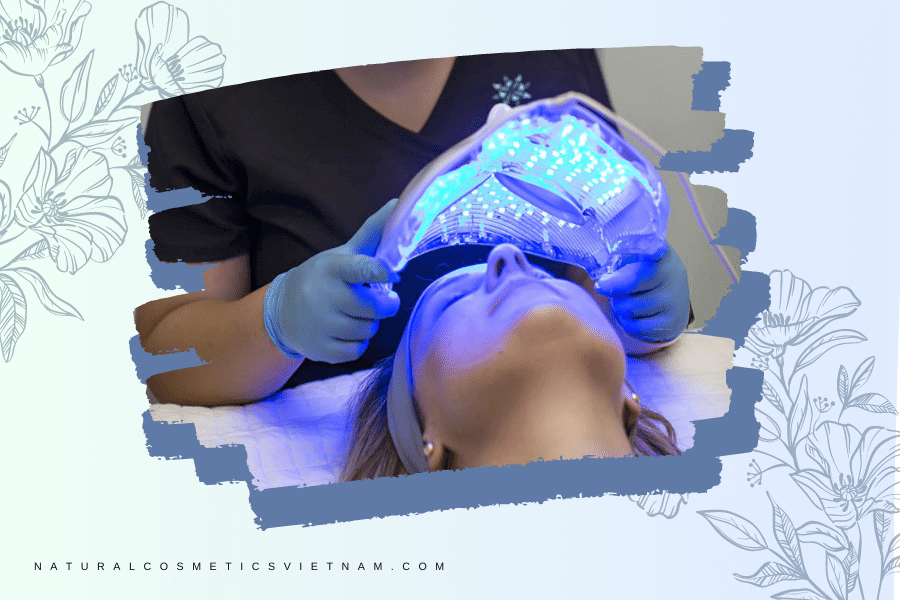
Skin Rejuvenation
Skin rejuvenation is a sought-after goal for many individuals seeking to improve the overall appearance and health of their skin. While traditional methods such as creams, serums, and invasive procedures have been popular, there is a growing interest in the potential benefits of using blue light therapy for skin rejuvenation. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the use of blue light in skin rejuvenation, exploring its benefits, considerations, and associated technologies.
Blue light has shown promising results in rejuvenating the skin by stimulating collagen production, reducing inflammation, and addressing certain dermatological conditions. Blue light has been found to penetrate the skin’s surface and stimulate fibroblast cells, which are responsible for producing collagen and elastin. This stimulation promotes the growth of new, healthy collagen fibers, leading to improved skin texture, firmness, and overall rejuvenation. It also has shown potential in reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation, including sunspots, age spots, and melasma. The targeted light energy helps break down excess melanin and even out skin tone, resulting in a more youthful and radiant complexion.
Considerations and Safety Precautions:
- Eye Protection: Blue light therapy requires eye protection as exposure to high-intensity blue light can be harmful to the eyes. Proper eye shields or goggles should be worn during the treatment to ensure safety.
- Treatment Duration and Frequency: The duration and frequency of blue light therapy sessions will vary depending on the specific skin concern and treatment protocol. It is important to follow the recommendations of a qualified skincare professional to achieve optimal results while minimizing potential side effects.
- Combination Therapy: Blue light therapy is often used in combination with other treatments, such as topical creams or serums, to enhance its effectiveness. Combining different modalities can provide synergistic benefits and maximize the overall rejuvenation outcomes.
- Skin Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience temporary redness, dryness, or sensitivity after blue light therapy. This is typically mild and subsides within a few hours to days. Proper skincare post-treatment, including moisturization and sun protection, is essential to support the healing process.
Blue light therapy has emerged as a promising tool in the field of skin rejuvenation. Its ability to stimulate collagen production, treat acne, and improve skin tone makes it a valuable option for individuals seeking non-invasive and effective skin rejuvenation treatments. However, it is important to consult with a qualified skincare professional to determine the suitability of blue light therapy for individual skin concerns and to ensure the highest level of safety and efficacy.
Exploring Its Applications in Skincare
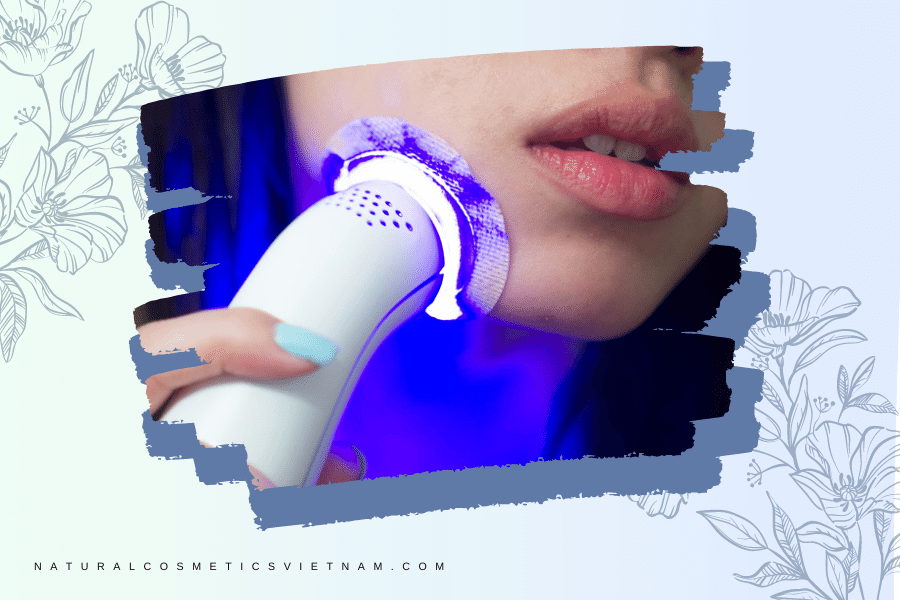
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by the excessive production of melanin, resulting in dark patches or spots on the skin. Various treatment options are available to address hyperpigmentation, and one emerging approach is the use of blue light therapy. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the use of blue light in treating hyperpigmentation, examining its mechanisms, efficacy, and important considerations.
Blue light therapy involves the application of specific wavelengths of blue light to target and reduce hyperpigmentation. Blue light penetrates the skin’s surface and works by breaking down excess melanin, the pigment responsible for dark spots. This targeted approach offers a non-invasive and potentially effective solution for managing hyperpigmentation.
Mechanisms of Action:
- Melanin Absorption: Blue light is absorbed by melanin, leading to a process called photothermolysis. This absorption generates heat that selectively targets melanin-containing cells, such as melanocytes, without causing significant damage to surrounding tissues.
- Melanin Disruption: The absorbed blue light energy disrupts the functioning of melanocytes, inhibiting melanin production and promoting the breakdown of existing melanin deposits. Over time, this can lead to a reduction in hyperpigmentation and a more even skin tone.
The duration and frequency of blue light therapy sessions for hyperpigmentation may vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual skin characteristics. A treatment plan customized by a qualified skincare professional is essential to optimize results. Blue light therapy can be combined with other treatments, such as topical depigmenting agents or chemical peels, to enhance outcomes. Combination therapy approaches can address hyperpigmentation through multiple pathways, providing comprehensive and synergistic effects. Following blue light therapy, it is crucial to protect the skin from excessive sun exposure and maintain a consistent skincare routine. Sunscreen application, moisturization, and avoiding direct sunlight during peak hours are vital to prevent further hyperpigmentation and maintain the treatment’s effectiveness.
While blue light therapy shows promise for various types of hyperpigmentation, it may not be suitable for all individuals. Factors such as skin type, sensitivity, and the underlying cause of hyperpigmentation should be considered when determining the appropriateness of blue light therapy.
Blue light therapy presents a promising option for the treatment of hyperpigmentation, offering a non-invasive approach that targets melanin without damaging surrounding tissues. By disrupting melanin production and promoting its breakdown, blue light therapy can contribute to a more even skin tone and reduced hyperpigmentation. However, it is crucial to consult with a skincare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan and ensure the highest level of safety and efficacy. With proper patient selection, individualized treatment protocols, and post-treatment care, blue light therapy holds significant potential as an effective tool in the management of hyperpigmentation.
Exploring Its Applications in Skincare
Oil Control
Excessive oil production is a common concern for many individuals, as it can lead to a shiny complexion, clogged pores, and an increased risk of acne breakouts. In recent years, blue light therapy has emerged as a potential solution for oil control in skincare. This article aims to delve into the use of blue light for oil control, exploring its mechanisms, efficacy, and considerations for incorporating it into a comprehensive skincare routine.
Blue light therapy involves the application of specific wavelengths of blue light to target and regulate sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing sebum, the skin’s natural oil. By modulating sebum production, blue light therapy offers a non-invasive approach to address oily skin concerns and promote a more balanced complexion.
Mechanisms of Action:
- Sebum Regulation: Blue light at wavelengths between 415 to 455 nanometers penetrates the skin and reaches the sebaceous glands. This targeted exposure to blue light helps regulate sebum production by suppressing the activity of sebocytes, the cells responsible for sebum synthesis.
- Antibacterial Properties: Blue light possesses inherent antibacterial properties, particularly against the bacteria associated with acne, such as Propionibacterium acnes. By reducing the presence of these bacteria, blue light therapy can contribute to the prevention of acne breakouts often associated with excessive oil production.
The duration and frequency of blue light therapy sessions for oil control may vary depending on individual skin characteristics, oil production levels, and desired outcomes. It is recommended to consult with a skincare professional to determine an appropriate treatment plan tailored to specific needs. Blue light therapy can be combined with other treatments, such as topical products containing oil-regulating ingredients or laser therapies, to enhance its effectiveness. This combination approach can address multiple factors contributing to oily skin, resulting in improved oil control and overall skin health. After undergoing blue light therapy for oil control, it is essential to follow a consistent skincare routine to maintain the results. This may include using oil-free or oil-controlling skincare products, practicing proper hygiene, and avoiding pore-clogging cosmetics or heavy moisturizers.
While blue light therapy holds promise for oil control, it may not be suitable for everyone. Factors such as skin type, sensitivity, and the underlying causes of excessive oil production should be considered when determining the appropriateness of blue light therapy.
Blue light therapy offers a promising avenue for managing excessive oil production and promoting oil control in skincare. By regulating sebum production and possessing antibacterial properties, blue light therapy can help achieve a more balanced complexion and reduce the risk of acne breakouts associated with oily skin. However, individualized treatment plans, combination therapies, and post-treatment care are crucial for maximizing the efficacy of blue light therapy for oil control. Consultation with a skincare professional is advised to determine the most suitable approach and ensure optimal results in achieving oil-free, healthier-looking skin.
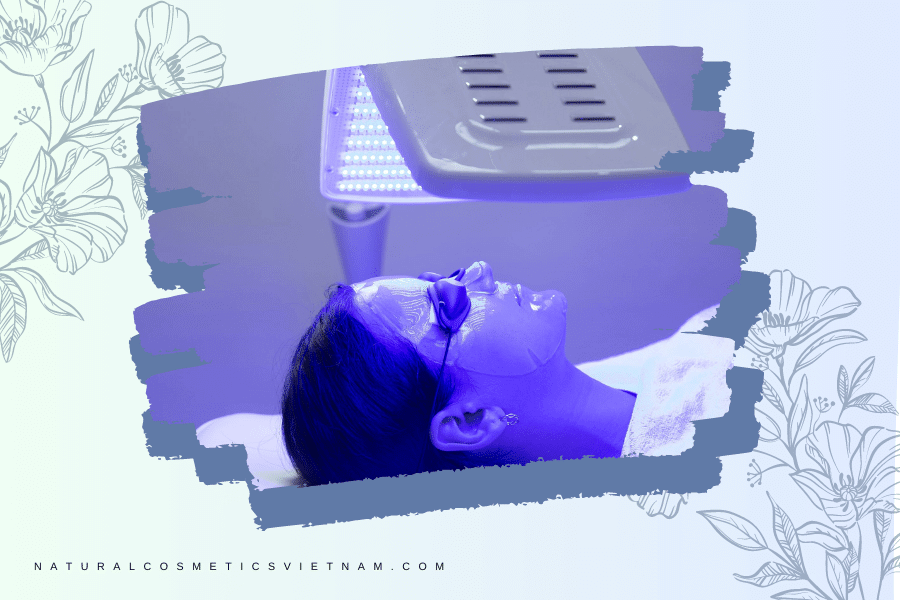
Exploring Its Applications in Skincare
Wound Healing
Wound healing is a complex process that involves various stages, including inflammation, tissue formation, and remodeling. In recent years, researchers have been investigating the potential of blue light therapy as a non-invasive and effective approach to enhance wound healing. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the use of blue light in wound healing, including its mechanisms of action, benefits, and considerations for its application.
Blue light therapy activates photoreceptors in cells and triggers a cascade of cellular responses. This process, known as photobiomodulation, promotes cellular proliferation, migration, and differentiation, all of which are crucial for wound healing. Blue light has been shown to possess antimicrobial properties, particularly against bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which are common pathogens in wound infections. By reducing bacterial load, blue light therapy helps create an environment conducive to optimal wound healing.
Benefits of Blue Light Therapy in Wound Healing:
- Accelerated Healing: Studies have demonstrated that blue light therapy can accelerate the healing process by promoting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), increasing collagen synthesis, and enhancing epithelialization (the formation of new skin over the wound).
- Reduced Inflammation: Blue light has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects, helping to control excessive inflammation at the wound site. By modulating the inflammatory response, blue light therapy can prevent complications and support the healing process.
- Pain Management: Blue light therapy has shown potential in reducing pain associated with wounds. Its analgesic properties make it a valuable adjunct therapy in wound management, providing relief and improving the overall patient experience.
The success of blue light therapy in wound healing depends on various factors, including the appropriate wavelength, intensity, duration, and frequency of treatment. These parameters may vary based on the specific wound type, location, and individual patient characteristics. Further research is needed to establish standardized protocols for effective blue light therapy in wound healing. Blue light therapy can be combined with other modalities, such as dressings, growth factors, and antimicrobial agents, to enhance wound healing outcomes. Synergistic approaches can address multiple aspects of the wound healing process and promote better overall results.
While blue light therapy is generally considered safe, proper eye protection should be used to prevent potential retinal damage. Additionally, individual patient factors, such as photosensitivity or underlying medical conditions, should be taken into account when considering blue light therapy for wound healing.
Blue light therapy holds significant promise as a non-invasive and effective approach to enhance wound healing. Its ability to promote cellular responses, reduce inflammation, and combat bacterial infections makes it a valuable addition to wound management strategies. However, further research is needed to optimize treatment parameters, establish standardized protocols, and explore its potential in combination therapies. As the understanding of blue light therapy continues to evolve, it has the potential to revolutionize wound care and improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
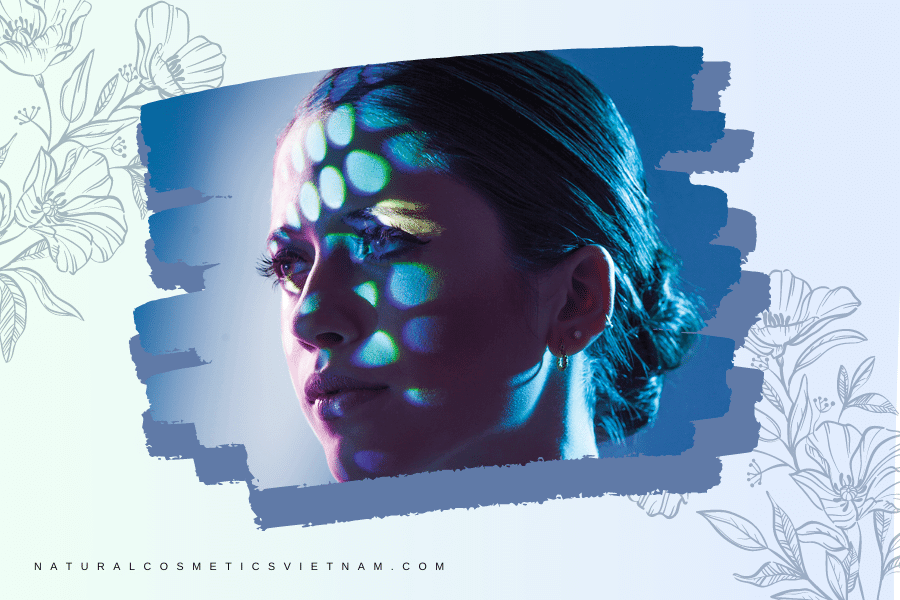
Exploring Its Applications in Skincare
Disclaimer
The information in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Please consult with a qualified dermatologist or skincare professional for personalized recommendations based on your specific skin concerns and needs.
FAQ
How does blue light affect your skin?
Recent research has shed light on the potential impact of overexposure to blue light emitted from electronic devices, such as computer and cell phone screens, on the aging process of our skin. Some studies suggest that extended exposure to blue light can lead to skin aging similar to that induced by UVA rays. However, in 2021, new research emerged challenging the notion that blue light from high-energy visible (HEV)-emitting devices is the primary culprit. Instead, it highlights solar blue light as a significantly greater concern when it comes to skin aging and damage.
In addition to the direct effects on the skin, another theory suggests that the use of blue-light-emitting devices at night, on a regular basis, or for prolonged periods can disrupt our sleep patterns and disturb our Circadian cycle, also known as our biological clock. Sleep plays a crucial role in allowing our bodies to enter a state of downtime, during which cellular repair and renewal processes are promoted. Disruption of this natural rhythm due to blue light exposure may indirectly contribute to premature skin aging by impeding the normal functioning of skin cells.
While these findings present intriguing insights into the potential effects of blue light on the skin, further research is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms involved and the extent of the impact. As the scientific community delves deeper into this subject, it is essential to stay informed and consider incorporating protective measures, such as minimizing blue light exposure during nighttime device usage, ensuring adequate sleep, and adopting a comprehensive approach to skincare that encompasses various factors influencing skin health.
Do antioxidants protect from blue light?
While antioxidants may not provide direct protection against blue light, their role in mitigating potential damage caused indirectly by blue light wavelengths should not be overlooked. Emerging research suggests that when blue light is absorbed through the skin, it can disrupt the natural functioning of our skin cells by deceiving their inner ‘bio-clock’. As a result, the cells’ regular downtime, during which they would typically engage in vital repair and renewal processes, is reduced.
This interference with the cellular bio-clock may diminish the cells’ ability to effectively address issues like free radical damage and other signs of premature skin aging. However, incorporating skincare products that contain antioxidants can help counteract this potential damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants have been widely recognized for their ability to neutralize free radicals and minimize the oxidative stress they can inflict on the skin.
By including antioxidant-rich ingredients in skincare formulations, we can bolster the skin’s natural defense mechanisms and support its resilience against the detrimental effects of blue light exposure. While further research is necessary to fully understand the precise mechanisms at play, the inclusion of antioxidants in skincare routines holds promise in mitigating the indirect impact of blue light on the skin and promoting overall skin health.
How can I learn to formulate skincare using antioxidants?
Formula Botanica is a renowned institution that offers a range of exceptional online courses designed to empower individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to become proficient formulators. Whether you aspire to create your own line of natural skincare or haircare products, their comprehensive courses will guide you through every step of the formulation process.
One of the fundamental aspects covered in these courses is the study of active ingredients, including the fascinating realm of antioxidants. Understanding the properties and functions of antioxidants is essential for formulators looking to develop effective and innovative natural products. With the guidance of Formula Botanica’s expert instructors, you will delve into the science behind antioxidants, exploring their diverse range of benefits and discovering how to harness their potential within your formulations. The curriculum provided by Formula Botanica goes beyond theoretical knowledge, offering practical insights and hands-on experience in formulating your own natural products. You will learn how to select the right ingredients, formulate with precision, and create customized skincare and haircare formulations that cater to specific needs and preferences.
By joining Formula Botanica’s esteemed community of students, you will gain access to a wealth of resources, including comprehensive learning materials, interactive assignments, and ongoing support from industry experts. The institution’s commitment to excellence and innovation has earned them accolades, making them a trusted source for aspiring formulators worldwide.
Embark on an exciting journey of exploration and creativity by enrolling in Formula Botanica’s online courses. Unlock your potential as a formulator, acquire invaluable skills, and embark on a fulfilling career in the dynamic world of natural skincare and haircare product development.
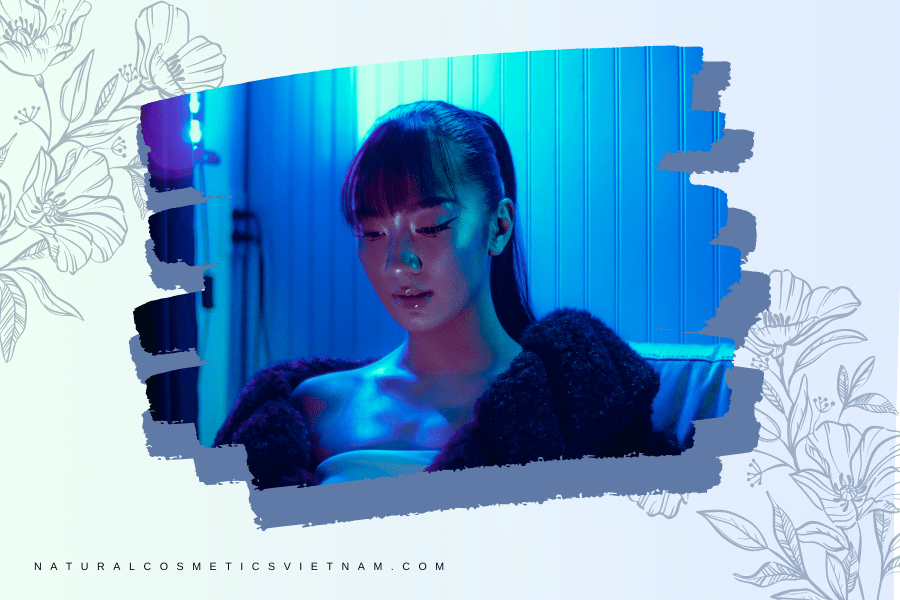
Blue Light Skincare
Is blue light only in electronics?
Blue light is not exclusive to electronic devices, but it is commonly emitted by them. In addition to electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computer screens, blue light is also present in natural sunlight. The blue light component of sunlight is a significant source of blue light exposure for humans.
When it comes to electronic devices, their screens often emit blue light as a byproduct of the technology used to produce the display. LED screens, in particular, emit higher amounts of blue light compared to other light sources. This is why the use of electronic devices, especially during evening hours or in low-light conditions, has been associated with potential disruptions to sleep patterns and the body’s circadian rhythm. It’s worth noting that exposure to blue light from electronic devices is a relatively recent phenomenon, driven by the increasing prevalence of digital technology in our lives. Before the advent of electronic devices, natural sunlight remained the primary source of blue light exposure for humans.
It is important to recognize that blue light, regardless of its source, can have both positive and negative effects on our health. Natural sunlight, for instance, plays a crucial role in regulating our circadian rhythm and promoting the production of vitamin D. However, excessive or improper exposure to blue light, whether from electronic devices or sunlight, has raised concerns regarding its potential impact on eye health, sleep patterns, and skin health.
Research in this field is ongoing, aiming to better understand the specific effects of blue light exposure from different sources and develop strategies to mitigate any potential risks. It is essential for individuals to be mindful of their blue light exposure and adopt healthy habits, such as reducing screen time before bedtime, using blue light filters or glasses when necessary, and seeking a balance between natural sunlight exposure and adequate protection to maintain overall well-being.
Should I use sunscreen all day until I don’t use the lights?
Using sunscreen throughout the day, even when not using artificial light, can provide additional protection against harmful UV radiation from natural sunlight. Sunscreen is designed to shield the skin from the damaging effects of the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays, which can cause sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. While artificial light sources, such as lamps and electronic devices, do emit some levels of UV radiation, the intensity is typically much lower compared to direct sunlight. Therefore, the primary concern when it comes to sunscreen usage is protecting the skin from the sun’s UV rays rather than the minimal UV exposure from artificial light sources.
It is recommended to apply sunscreen daily, regardless of whether you will be exposed to artificial light or sunlight. Even on cloudy or overcast days, UV radiation can still penetrate the clouds and reach the Earth’s surface, potentially causing skin damage. Additionally, certain indoor environments, such as offices or homes with large windows, may allow UV rays to enter and affect the skin. When choosing a sunscreen, it is advisable to select a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, it is essential to follow the instructions on the product, including reapplying sunscreen every two hours or more frequently if sweating or swimming.
Ultimately, using sunscreen throughout the day, even when not using artificial light, can help maintain consistent sun protection and reduce the risk of skin damage from UV radiation. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide personalized recommendations on sunscreen usage based on individual skin type, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
While using sunscreen throughout the day is generally recommended for sun protection, there can be potential drawbacks to consider. Here are a few downsides:
- Skin Sensitivity: Some individuals may have sensitive skin that can react negatively to certain sunscreen ingredients. This can lead to skin irritation, redness, or breakouts. It’s important to choose a sunscreen that suits your skin type and consider patch testing new products before applying them all over the face or body.
- Using sunscreen for an extended period can potentially clog the pores and lead to skin congestion. This is because sunscreen products often contain oils, emollients, or other ingredients that can contribute to pore blockage if not properly cleansed from the skin. It is essential to cleanse the skin thoroughly at the end of the day to remove any sunscreen residue and prevent the buildup of excess oils or impurities. Regular exfoliation and a consistent skincare routine can also help prevent pore congestion and maintain healthy skin.
- Chemical Sunscreen Ingredients: Certain chemical sunscreen ingredients, such as oxybenzone or avobenzone, have raised concerns about their potential to disrupt hormones or cause allergic reactions in some people. If you have specific sensitivities or concerns, you may opt for physical/mineral sunscreens containing ingredients like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
- Dependency on Sunscreen: Relying solely on sunscreen for sun protection may give a false sense of security. Sunscreen should be used in conjunction with other protective measures like seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and using hats or sunglasses. Over-reliance on sunscreen alone may lead to increased sun exposure or neglect of other sun safety practices.
- Vitamin D Synthesis: Sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) can limit the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. While it’s important to protect the skin, adequate vitamin D levels are also necessary for overall health. If you have concerns about vitamin D deficiency, you may consider short periods of unprotected sun exposure or consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
- Environmental Impact: Some chemical sunscreen ingredients can have detrimental effects on marine ecosystems when they enter water bodies through swimming or during showering. Certain regions have banned or restricted the use of specific sunscreen ingredients to protect coral reefs and other marine life. Opting for reef-safe or environmentally friendly sunscreen options can help minimize environmental impact.
It’s important to weigh the potential risks and benefits of using sunscreen and make informed decisions based on individual circumstances. Consulting with a dermatologist or healthcare professional can provide personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and concerns.









Leave a reply